Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology have undeniably emerged as groundbreaking innovations with the potential to reshape various industries, most notably finance. While terms like Bitcoin and Ethereum frequently make headlines, understanding their underlying technology and the inherent risks of investing in them is crucial for anyone looking to step into this volatile yet promising new world.
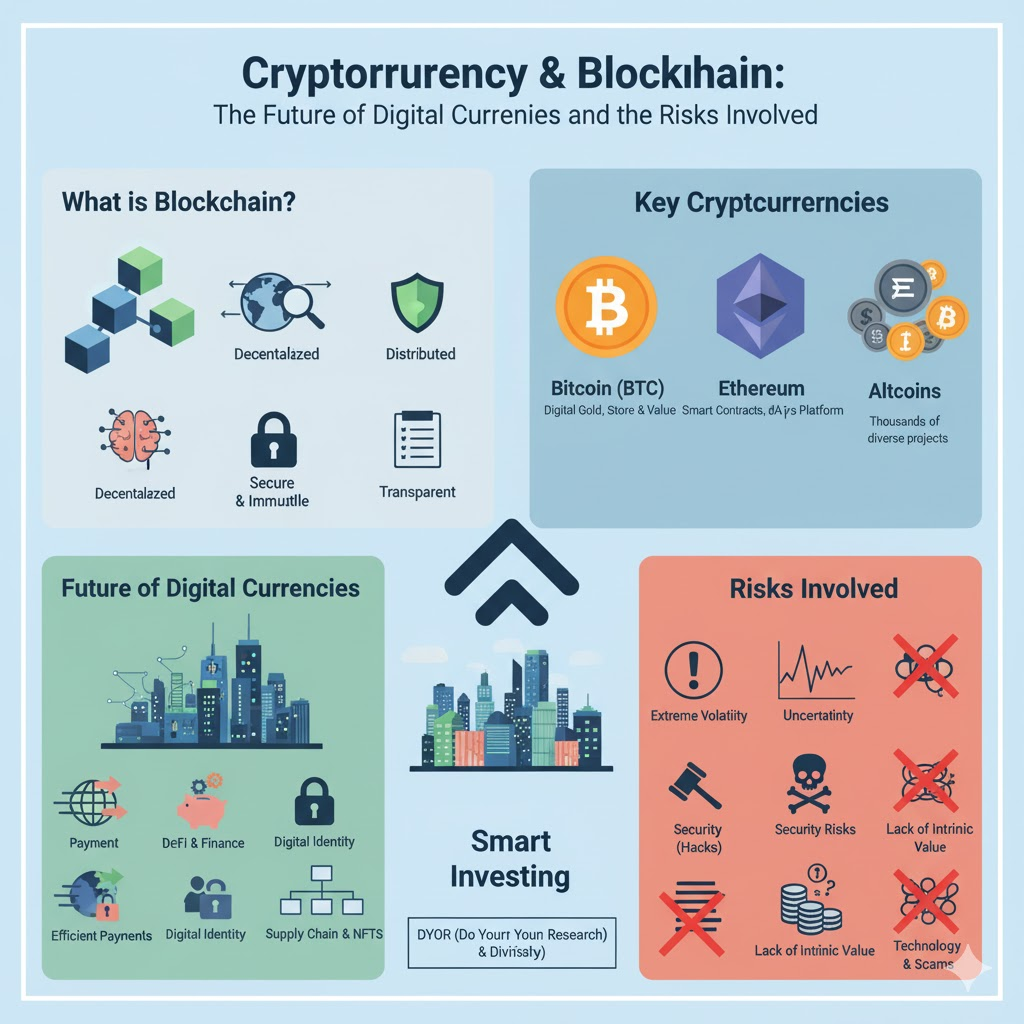
What is Blockchain? The Foundation
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed, and immutable ledger. Imagine a digital spreadsheet that is copied and spread across thousands of computers globally. Every time a new transaction occurs, it’s added to a “block,” and once that block is verified and complete, it’s permanently added to the “chain” of previous blocks.
Key characteristics of Blockchain:
- Decentralized: No single entity controls the network. This removes the need for intermediaries like banks.
- Distributed: All participants on the network have a copy of the ledger.
- Immutable: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted.
- Transparent: All transactions are publicly visible (though often pseudonymous, meaning associated with an address, not a real name).
- Secure: Cryptographic techniques protect transactions and link blocks, making it incredibly difficult to hack.
What is Cryptocurrency? The Application
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security and operate on blockchain technology. They are designed to be a medium of exchange, secure by nature, and often decentralized.
Key Players:
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, often called “digital gold.” Primarily designed as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system.
- Ethereum (ETH): The second-largest cryptocurrency. Beyond being a digital currency, Ethereum introduced “smart contracts” – self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This allows for decentralized applications (dApps) to be built on its platform.
- Altcoins: This term refers to any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. There are thousands of altcoins, each with unique features and use cases (e.g., Litecoin, Ripple, Cardano, Solana).
The Future of Digital Currencies
Cryptocurrency and blockchain are driving significant changes and promise a future with:
- More Efficient Payments: Faster and cheaper international transactions, bypassing traditional banking fees and delays.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Financial services (lending, borrowing, insurance) built on blockchain, removing intermediaries and offering more transparent, accessible options.
- Digital Identity: Secure, self-sovereign digital identities that give individuals more control over their personal data.
- Supply Chain Management: Enhanced transparency and traceability for goods from origin to consumer.
- New Forms of Ownership: NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are enabling digital ownership of art, music, and other assets.
- Programmatic Money: Smart contracts allow money to be programmed to execute based on specific conditions, opening up innovative applications.
Risks Involved in Investing in Cryptocurrencies
Despite their potential, cryptocurrencies are highly speculative and volatile investments. It’s crucial to be aware of the significant risks:
- Extreme Volatility: Crypto prices can swing wildly in short periods, leading to substantial gains or losses.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still grappling with how to regulate cryptocurrencies. New laws could impact their value and usability.
- Security Risks (Hacks & Scams): While blockchain itself is secure, exchanges and individual wallets can be vulnerable to hacks, phishing, and various scams (e.g., rug pulls, pump-and-dumps).
- Lack of Intrinsic Value (for some): Unlike traditional assets like stocks (which represent ownership in a company) or bonds (which offer interest payments), many cryptocurrencies’ value is driven purely by speculation and market demand.
- Complex Technology: Understanding the underlying technology can be challenging, making it hard for new investors to differentiate between legitimate projects and hyped-up scams.
- Liquidity Issues: Some smaller cryptocurrencies may not have enough buyers or sellers, making it difficult to convert them back to traditional currency without impacting their price significantly.
- Irreversible Transactions: Blockchain transactions are irreversible. If you send crypto to the wrong address, it’s usually lost forever.
Investing Wisely: A Cautious Approach
If you choose to invest in cryptocurrencies, adopt a cautious strategy:
- Do Your Research (DYOR): Understand the project’s whitepaper, technology, team, and use case.
- Invest Only What You Can Afford to Lose: Consider crypto as a high-risk, high-reward part of your portfolio, not your entire savings.
- Diversify: Don’t put all your money into one cryptocurrency.
- Secure Your Assets: Use reputable exchanges, strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and consider hardware wallets for larger holdings.
- Long-Term Perspective: Avoid trying to “get rich quick.” Focus on projects with long-term potential.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency and blockchain are revolutionary technologies that are here to stay, promising a more decentralized and efficient future. While the potential rewards are significant, the risks are equally substantial. For newcomers, a thorough understanding of the technology, a clear awareness of the risks, and a disciplined, well-researched approach are paramount to navigating this exciting, yet challenging, financial frontier.